Have you ever wondered why some plants thrive in your garden while others struggle? The secret often lies beneath your feet—in the soil.
Understanding the type of soil in your region can transform your gardening experience, helping you choose the right plants and improve your garden’s health. Imagine having a lush, thriving garden without constant frustration. By learning how to identify your soil type, you’ll unlock the potential for a more productive and beautiful garden.
Curious to discover the hidden characteristics of your soil and how they impact your gardening success? Keep reading to uncover the simple steps to soil identification that will empower you to make smarter gardening decisions.
Common Soil Types
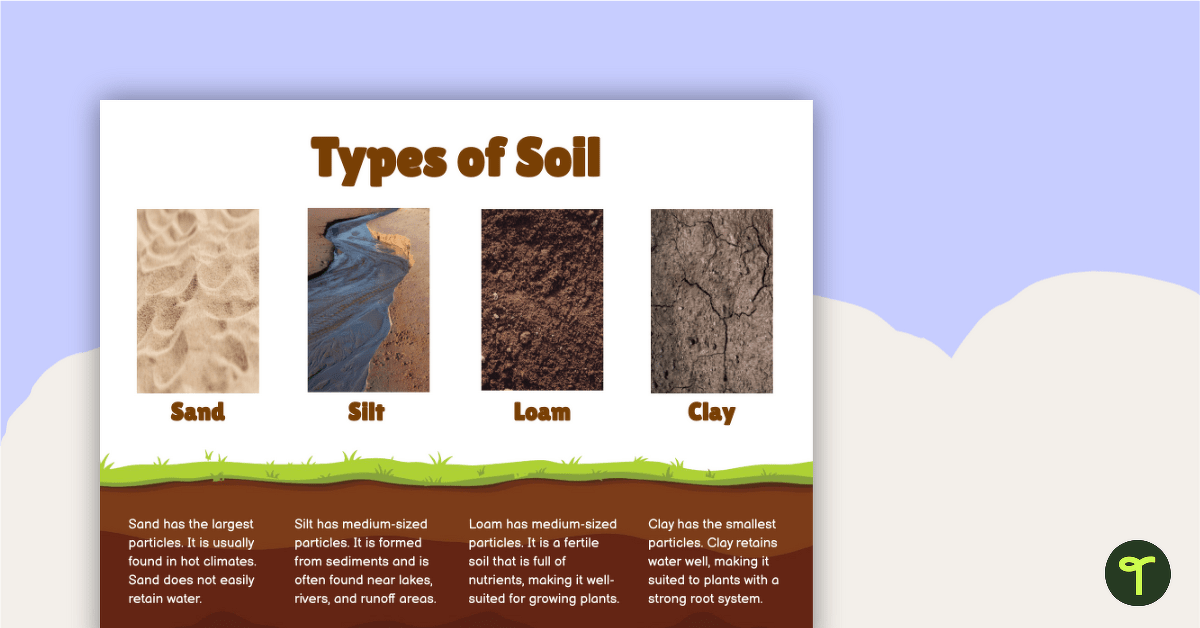
Identifying soil types helps in understanding local gardening needs. Clay soils feel sticky and hold water well. Sandy soils feel gritty and dry quickly. Loamy soils balance moisture and drainage, ideal for most plants. Observing texture and color aids in classification.
Understanding the common soil types in your region can help you make informed decisions about gardening, farming, or landscaping. Each soil type has unique properties that affect drainage, nutrient availability, and plant compatibility. Let’s explore some of the most prevalent soil types you might encounter.Loamy Soil
Loamy soil is often considered the ideal type for gardening. It is a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, providing good drainage and nutrient retention. If you’ve ever dug into a garden bed and found a soil that feels crumbly yet retains moisture, you’ve likely encountered loamy soil.Sandy Soil
Sandy soil is gritty and drains quickly. It’s perfect for plants that don’t like “wet feet,” such as succulents and certain herbs. However, it can be challenging to keep nutrients in sandy soil, so regular fertilization might be needed. Have you ever noticed how quickly water disappears from the soil at a beach? That’s because sand doesn’t hold water well.Clay Soil
Clay soil is dense and holds water well, but it can become compacted easily. This soil type is great for plants that enjoy moist conditions, like certain types of perennials. However, clay can be a challenge to work with, especially when wet. If your shovel sticks and the soil feels heavy, you’re likely dealing with clay.Silty Soil
Silty soil has a smooth texture and retains moisture, making it rich in nutrients. It’s great for growing a wide range of plants but can become waterlogged if not managed properly. Have you ever walked by a riverbank and felt the fine, slippery soil beneath your feet? That’s the texture of silt.Peaty Soil
Peaty soil is dark and rich in organic matter, often found in marshy areas. It’s acidic, which can be beneficial for acid-loving plants like blueberries. Peaty soil can be tricky, though, as it may require drainage improvements. If you’ve ever noticed a soil that feels spongy and smells like decomposing plants, that’s peat.Chalky Soil
Chalky soil is alkaline and often contains visible white stones. This soil type can be challenging for acid-loving plants but is perfect for those that thrive in alkaline conditions, such as lilacs. If your garden soil has a whitish tinge and feels coarse, you might be working with chalky soil. Understanding these soil types can transform your gardening efforts. Which soil type do you think is most common in your backyard, and how might it affect your planting choices? By identifying the soil type, you can enhance your garden’s productivity and beauty.Physical Characteristics
Different soil types can be identified by their texture, color, and moisture retention. Clay soil feels sticky, sandy soil feels gritty, and loamy soil is smooth. Observing these characteristics helps determine the soil type in your region.
Understanding the physical characteristics of soil is essential for any gardener or farmer. It helps you choose the right plants for your soil type and improve your gardening results. By examining these features, you can gain valuable insights into the health and composition of your soil. ###Texture
Soil texture refers to the size of the particles in your soil. This can range from sandy (large particles) to clay (small particles). You can perform a simple test by moistening a small amount of soil and rubbing it between your fingers. Sandy soils feel gritty, while clay soils feel sticky. Loam, often considered the ideal soil type, is a balanced mix that feels smooth. ###Color
Soil color can tell you a lot about its composition and fertility. Dark brown or black soils are usually rich in organic matter, which is great for plant growth. Red or yellow soils might indicate the presence of iron oxides, suggesting good drainage but possible nutrient deficiencies. Testing your soil’s color can give you clues about its health and how you might improve it. ###Structure
Soil structure refers to how soil particles group together. Good soil structure allows air and water to move freely, which is crucial for root growth. If your soil is loose and crumbles easily, it likely has a good structure. Compacted soil, on the other hand, forms hard clumps and can restrict plant growth. Consider aerating your soil if it seems too compacted. ###Drainage
How well does your soil drain? This is a vital question for plant health. To check, dig a small hole and fill it with water. If it drains quickly, your soil has good drainage. If water pools or drains slowly, you may need to amend your soil with organic material to improve its permeability. Poor drainage can lead to root rot and other plant issues. ###Consistency
Consistency refers to how soil behaves under different moisture conditions. Dry soil might be crumbly, while wet soil can be either sticky or slippery. By observing how your soil changes with moisture, you can better manage watering schedules and choose suitable plants. Knowing your soil’s consistency helps you maintain optimal growing conditions. Engaging with your soil’s physical characteristics is a hands-on way to connect with your garden. Have you ever noticed how different your backyard soil feels compared to a friend’s garden? These little observations can lead to big improvements in how you manage your plants. What surprising things have you discovered by just getting your hands dirty?Testing Techniques
Discovering soil types in your region involves simple tests. Feel the soil for texture and moisture. Observe color variations, and notice how it drains after rain. These clues help identify sandy, clay, or loamy soil types effectively.
Understanding the type of soil in your region is crucial for successful gardening and farming. Testing techniques are the best way to accurately determine your soil type. You might be wondering how you can carry out these tests without specialized equipment or scientific expertise. Let’s dive into some practical methods you can use to identify your soil type right from your backyard.1. The Jar Test
The jar test is simple yet effective. Fill a jar with soil and water, then shake it well. Let it sit for 24 hours. You’ll notice the soil settles into layers: sand at the bottom, silt in the middle, and clay on top. By observing the proportions of each layer, you can determine your soil type. Have you ever tried this with a mason jar you have at home?2. The Squeeze Test
This tactile test requires no tools, just your hands. Take a handful of moist soil and squeeze it tightly. Does it crumble, form a loose ball, or feel sticky? If it crumbles, you likely have sandy soil. A loose ball suggests loamy soil, whereas stickiness indicates clay. Can you feel the difference between the textures?3. Ph Test Strips
Soil pH affects plant growth, so it’s essential to know it. Use pH test strips, which are affordable and easy to use. Mix soil with distilled water, dip the strip in, and compare the color to the chart provided. An acidic soil will show a lower pH, while a higher pH indicates alkalinity. How does your soil measure up?4. The Ribbon Test
This method involves rolling soil into a ribbon between your fingers. The longer the ribbon before breaking, the more clay content your soil has. A short ribbon suggests sandy soil, while a medium length indicates loamy soil. Have you ever noticed how some soils feel like playdough while others fall apart?5. Soil Color Observation
Soil color can tell you a lot about its composition and health. Dark soil typically has more organic matter, which is great for plant growth. Lighter soil might indicate sand or low fertility. Next time you dig in your garden, take a moment to observe the color. What does it tell you about your soil’s health? Testing your soil is not just about understanding its type but also about connecting with your land. Each test offers insights that can transform your gardening experience. Have you discovered anything surprising about your soil using these techniques?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ms-usda-gardening-zone-3a925f9738ce4122b56cde38d3839919.jpg)
Regional Variations
Understanding soil types in your region is crucial for successful gardening. Each region offers unique soil characteristics that impact plant growth. By learning about these regional variations, you can select the best plants for your soil. This knowledge helps in improving soil health and productivity.
Understanding Sandy Soils
Sandy soils are common in coastal areas and deserts. These soils drain quickly, making them dry out fast. To improve sandy soil, add organic matter like compost. This helps retain moisture and nutrients.
Recognizing Clay Soils
Clay soils are found in regions with high rainfall. They hold water well, but can become compacted. This makes it difficult for roots to grow. Breaking up clay soil with organic material improves drainage and aeration.
Identifying Silt Soils
Silt soils are smooth and powdery when dry. They are often found in river valleys and floodplains. These soils retain moisture and nutrients but can erode easily. Plant cover crops to prevent erosion and enrich the soil.
Exploring Loam Soils
Loam soils are ideal for gardening and farming. They contain a balance of sand, silt, and clay. Loam soils are fertile and easy to work with. They provide good drainage and retain moisture well. Test your soil to determine its composition.
Spotting Peaty Soils
Peaty soils are dark and rich in organic material. They are common in wetlands and boggy areas. Peaty soils hold a lot of water, so they drain slowly. Adding lime can help reduce acidity in peaty soils. This makes them suitable for more plant types.
Understanding Chalky Soils
Chalky soils are alkaline and often pale in color. They contain large amounts of calcium carbonate. These soils drain quickly and can lack nutrients. Use organic matter to improve soil structure and fertility.
Knowing your region’s soil type helps in choosing the right plants. It also aids in making necessary soil amendments. This knowledge empowers you to create a thriving garden.
Conclusion
Identifying soil types helps improve your gardening success. Each soil type affects plant growth differently. Test your soil using simple methods at home. Observe color, texture, and moisture. Clay, sand, and loam are common types. Understand your region’s soil for better planting choices.
Healthy soil supports vibrant gardens. Adjust your gardening techniques based on soil findings. Use compost and mulch to enrich poor soil. Soil knowledge leads to better gardening decisions. Explore local resources for more information. Happy gardening with the right soil insights!