Have you ever wondered how the food on your plate is connected to the climate changes happening around us? It’s more related than you might think.
Climate change isn’t just about rising temperatures or melting ice caps—it’s also impacting the very ground beneath our feet. The quality of soil is crucial for growing the nutritious food you and your family enjoy. But as climate patterns shift, our soil is facing new challenges.
The impact of these changes is far-reaching and could affect your grocery choices and even the planet’s future health. As you read on, you’ll discover the vital connection between climate change and soil quality, and why understanding this link is essential for everyone who values healthy living and a sustainable future. Don’t miss out on learning how these global shifts may affect your everyday life and what you can do about it.
Impact On Soil Nutrients
Climate change is altering the delicate balance of soil nutrients. These changes threaten plant growth and crop yields. Understanding this impact is crucial for sustainable agriculture.
Soil nutrients support plant health and productivity. Rising temperatures disrupt nutrient cycles. Heat speeds up the decomposition process. This leads to rapid nutrient loss.
Changes In Soil Composition
Increased rainfall affects soil structure. It washes away vital nutrients. Soil erosion becomes a major concern. Nutrient-rich topsoil is lost, reducing fertility.
Acidification Of Soil
Climate change increases soil acidity. Acid rain leaches essential nutrients. This weakens soil health. Acidic soils struggle to support diverse plant life.
Impact On Microbial Activity
Soil microbes are vital for nutrient cycles. Rising temperatures alter microbial activity. This affects nutrient availability. Soil health declines as microbial balance shifts.
Carbon And Nitrogen Imbalance
Carbon and nitrogen are crucial for plant growth. Climate change disrupts their balance. Excess carbon reduces nitrogen uptake. This hampers plant development.
Strategies For Soil Nutrient Management
Adapting farming practices is essential. Crop rotation helps maintain nutrient levels. Organic fertilizers improve soil health. These strategies ensure sustainable soil management.

Alterations In Soil Structure
Climate change is reshaping our world. One major impact is on soil. Soil structure changes can have huge effects on agriculture and ecosystems. The structure of soil refers to how its particles are organized. These changes can affect water retention, nutrient availability, and plant growth. Understanding these alterations can help us address the challenges they bring.
Changes In Soil Composition
Climate change can lead to soil erosion. This alters the composition. Erosion strips away the topsoil. This layer is rich in nutrients. Without it, plants struggle to grow. Increased rainfall intensity also contributes to erosion. The soil becomes compacted. This reduces its ability to absorb water.
Impact On Soil Porosity
Soil porosity is crucial for plant health. It determines how water and air move through soil. Climate change can reduce porosity. Higher temperatures dry out the soil. This makes it hard and compact. Poor porosity leads to reduced root growth. Plants cannot access the nutrients they need.
Effects On Soil Organic Matter
Soil organic matter is vital for soil fertility. It consists of decayed plant and animal material. Climate change can decrease this matter. Rising temperatures increase decomposition rates. This process releases carbon dioxide. The loss of organic matter reduces soil’s ability to hold water. It also affects its structure.
Disruption Of Soil Microbial Communities
Microbes play a key role in soil health. They help break down organic matter. Climate change disrupts these communities. Temperature shifts and moisture changes affect them. This can lead to a loss of biodiversity. Affected microbes can harm plant growth. Soil health declines as a result.
Effects On Soil Microorganisms
Climate change alters soil quality by disturbing microorganisms essential for nutrient cycles. Increased temperature and irregular rainfall patterns affect microbial activity and diversity. Soil health suffers, impacting plant growth and ecosystem stability.
Understanding how climate change impacts soil quality is crucial, especially when examining its effects on soil microorganisms. These tiny creatures play a vital role in maintaining the health of our soil, influencing everything from nutrient cycling to plant growth. As climate change progresses, shifts in temperature and moisture levels directly affect these microorganisms, with significant consequences for soil health.How Temperature Changes Affect Microbial Activity
Rising temperatures can speed up the metabolism of soil microorganisms. This might initially sound beneficial, but there’s a catch. Enhanced activity can lead to faster decomposition of organic matter, which depletes essential nutrients in the soil. During a summer hike, you might have noticed how warm the ground feels. This heat can disrupt the delicate balance microorganisms need to thrive. Have you considered how this might affect the plants and crops you rely on?Impact Of Altered Rainfall Patterns
Unpredictable rainfall, another result of climate change, can leave soil too wet or too dry. Both scenarios harm microorganisms. In waterlogged conditions, oxygen levels drop, making it hard for aerobic microorganisms to survive. Conversely, in drought conditions, microorganisms struggle to maintain their activity levels. Imagine watering your garden every day, only to see it flooded by unexpected rain. Such swings can wreak havoc on the soil life that supports plant growth.Soil Acidity And Microbial Health
As climate change alters atmospheric conditions, soil acidity can increase. Acidic soils can limit the diversity of microorganisms. Certain microbes can’t survive in low pH environments, reducing the soil’s ability to support diverse plant life. Have you tested the pH of your garden soil lately? It’s a simple action with significant implications for the health of your plants and the microorganisms that support them.Carbon Storage And Microbial Balance
Microorganisms play a key role in carbon storage by breaking down organic matter. Climate change, however, can disrupt this process. When the balance is off, less carbon is stored in the soil, contributing to higher carbon levels in the atmosphere. This cycle can exacerbate climate change. What steps can you take to ensure the microorganisms in your garden are maintaining a healthy carbon balance? Understanding these effects can help you make informed decisions about managing your soil. By taking proactive steps, you can support the microorganisms that play such a critical role in the ecosystem. Are you ready to take action to protect and nurture your soil’s health?
Consequences For Agriculture
Climate change is reshaping our planet in countless ways. One crucial area affected is soil quality, which directly impacts agriculture. Farmers worldwide face challenges due to altered soil conditions. This disruption threatens food security and livelihoods. Understanding these impacts is vital for developing sustainable farming practices.
1. Changes In Soil Composition
Rising temperatures alter soil chemistry. Essential nutrients become depleted. This nutrient loss reduces crop yields. Crops need balanced nutrients to thrive. Without them, growth is stunted. Farmers must adapt to these changing conditions.
2. Increased Soil Erosion
Extreme weather events lead to soil erosion. Heavy rains wash away topsoil. Windstorms blow loose soil particles. Erosion strips away fertile layers. This loss limits plant growth. Farmers need to find erosion control methods.
3. Altered Water Retention
Soil’s ability to retain water is changing. Warmer climates increase evaporation rates. Drier soil struggles to support crops. Water scarcity becomes a pressing issue. Irrigation demands rise, straining resources.
4. Impact On Soil Microbial Life
Microbes play a key role in soil health. They help decompose organic matter. Climate change alters microbial communities. Changes in temperature and moisture affect their balance. This disruption impacts nutrient cycling.
5. Rising Soil Salinity Levels
Increased salinity is a growing concern. Sea level rise introduces salt into coastal soils. Irrigation practices can worsen salinity. High salt levels harm plant growth. Farmers need strategies to manage soil salinity.
6. Threats To Crop Diversity
Climate change threatens crop diversity. Some plants can’t adapt to new conditions. This reduces the variety of crops grown. Limited diversity affects food availability. Farmers must explore resilient crop options.
7. Economic Implications For Farmers
Soil quality directly affects farm income. Poor soil leads to lower yields. Reduced production means less profit. Farmers face higher costs to adapt. This economic strain impacts rural communities.
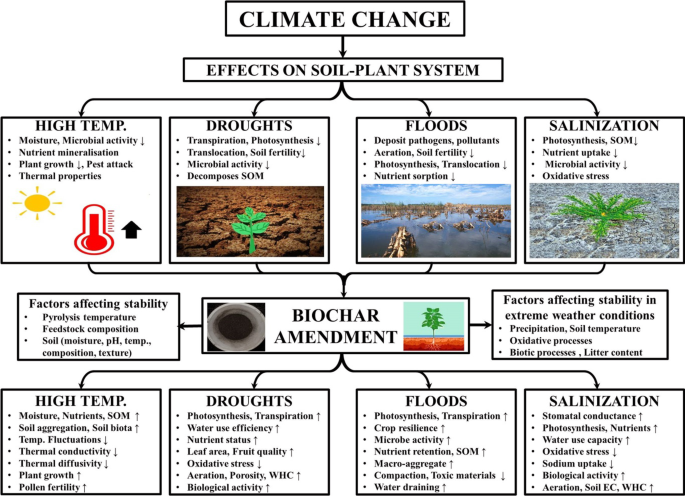
Conclusion
Soil quality suffers greatly due to climate change. Rising temperatures and erratic weather patterns disrupt nutrient balance. Poor soil quality affects crop yield and food security. It harms the ecosystem and biodiversity, too. Farmers face challenges in sustaining healthy soil.
Strategies exist to combat these effects. Using organic practices and soil conservation can help. Enhancing soil health is crucial for our future. Everyone’s effort counts in this fight. Simple changes can make a difference. Let’s work together to protect our soil.
For a healthier planet.