Imagine a world where your farm thrives despite changing weather patterns. Picture a future where your crops and livestock are more resilient, your yields are higher, and your income is more secure.
Climate-smart farming practices can turn this vision into reality for smallholders like you. By adopting these innovative strategies, you’re not just protecting your land; you’re ensuring a sustainable livelihood for your family and community. Curious to learn how you can transform your farm and future?
Keep reading to discover the powerful techniques that are reshaping agriculture and empowering smallholders across the globe.
Sustainable Soil Management
In the quest for climate-smart farming, sustainable soil management emerges as a cornerstone for smallholders. Healthy soil isn’t just dirt; it’s a living ecosystem that nourishes crops and sustains livelihoods. By adopting practices that improve soil health, small-scale farmers can boost productivity and resilience against climate change.
Understanding Soil Health
Think of soil as your farm’s foundation. It’s home to countless microorganisms that help break down organic matter, releasing nutrients essential for plant growth. When soil is healthy, plants thrive, pests are less of a problem, and water retention improves.
Your soil’s health reflects in your yield. If your crops struggle, look beyond fertilizers. Assess the soil’s texture, structure, and organic content. A simple soil test can reveal nutrient deficiencies that need attention.
Organic Matter: Your Soil’s Best Friend
Adding organic matter can transform your soil. Compost, plant residues, and manure enrich the soil, promoting microbial activity. They also help retain moisture, which is crucial during dry spells.
Consider starting a compost pile. It’s an easy way to recycle farm waste and improve soil fertility. Every time you add organic matter, you’re investing in the future of your farm.
Crop Rotation For Soil Balance
Planting the same crop repeatedly can deplete soil nutrients. Rotating crops breaks this cycle, preventing nutrient exhaustion. It also disrupts pest and disease cycles, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Imagine swapping your maize with legumes. Legumes fix nitrogen in the soil, enhancing its fertility naturally. This simple switch can lead to healthier crops and soil.
Cover Crops: Protecting And Enriching
Cover crops act as a protective blanket for your soil. They prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and add nutrients. Consider planting cover crops during the off-season to maintain soil health.
Have you tried using cover crops like clover or rye? They not only protect your soil but also improve its structure and fertility. These crops are a boon for any smallholder aiming for sustainable farming.
Minimal Tillage: Less Is More
Excessive tilling can harm soil structure and reduce its ability to hold water. Minimal tillage preserves soil integrity, keeping its ecosystem intact. This approach saves time and labor while ensuring soil health.
Reflect on your tillage practices. Could reducing them improve your soil’s health? You might find that less disturbance leads to more robust crop growth and better water management.
Are you ready to transform your farm with sustainable soil management? Each small change contributes to a bigger impact, empowering you to face climate challenges head-on. Share your experiences and insights, and let’s cultivate a community of climate-smart farmers.

Water Conservation Techniques
Water conservation is crucial for smallholder farmers. Climate-smart farming practices help manage water resources efficiently. These techniques ensure sustainable agriculture and improve crop yield. Let’s explore some effective methods.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting captures and stores rain for later use. Farmers can use tanks, barrels, or underground cisterns. Stored rainwater provides irrigation during dry periods. This reduces reliance on external water sources.
Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots. This method reduces water waste and evaporation. It ensures that plants receive the right amount of water. Smallholders benefit from increased efficiency and productivity.
Mulching
Mulching covers soil with organic or synthetic materials. This technique conserves moisture and reduces evaporation. Mulch also prevents weed growth and improves soil health. It is cost-effective and easy to implement.
Contour Farming
Contour farming involves plowing along the land’s contour lines. This practice reduces water runoff and soil erosion. It helps retain water in the soil. Farmers can plant crops on these natural terraces.
Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors monitor soil moisture levels. They provide real-time data for efficient irrigation. Farmers can adjust water usage based on sensor readings. This ensures optimal water use and prevents over-irrigation.
Cover Crops
Cover crops are planted to protect and enrich soil. They help retain moisture and reduce erosion. Cover crops improve soil structure and fertility. They enhance water conservation and support sustainable farming.
Agroforestry Benefits
Agroforestry is an ancient practice making a modern comeback. It integrates trees with crops and livestock. This method benefits smallholders in many ways. Trees can improve soil health and increase crop yields. They also provide shade and reduce soil erosion. Agroforestry supports biodiversity and offers additional income sources. Let’s dive into its benefits.
Environmental Sustainability
Agroforestry improves environmental health. Trees help in carbon sequestration. They absorb carbon dioxide from the air. This process combats climate change. Trees also prevent soil erosion. Their roots hold soil firmly. This reduces the loss of fertile topsoil. Additionally, trees provide shade. This lowers temperatures for plants and animals.
Enhanced Biodiversity
Trees in agroforestry attract various species. Birds, insects, and animals find shelter. They create a balanced ecosystem. This balance reduces pests naturally. It limits the need for chemical pesticides. A variety of plants and animals thrive together. This increases biodiversity in small farms.
Improved Soil Health
Trees improve soil structure. Their roots aerate the soil. This allows water and nutrients to reach plants. Trees also add organic matter. Fallen leaves decompose and enrich the soil. This creates a nutrient-rich environment for crops. Healthy soil leads to better crop yields.
Increased Economic Opportunities
Agroforestry provides multiple income streams. Farmers can sell timber and fruits. Some trees produce nuts and medicines. These products add to farm income. Livestock can graze under trees. This reduces feed costs. Agroforestry diversifies income sources for smallholders.
Climate Resilience
Agroforestry builds climate resilience. Trees buffer against extreme weather. They protect crops from wind and heavy rain. Trees also regulate local climates. They maintain moisture and temperature levels. This ensures stable farming conditions. Smallholders can rely on more consistent harvests.

Conclusion
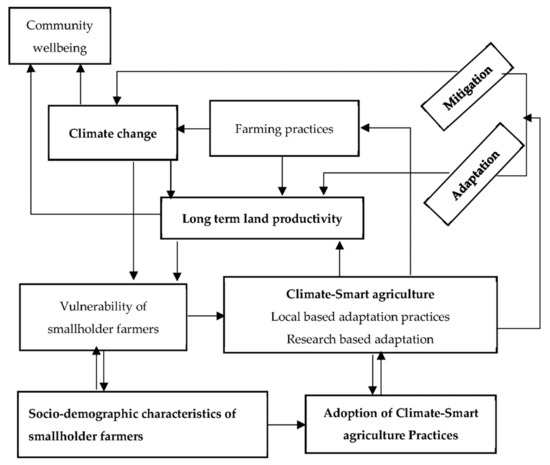
Smallholders can greatly benefit from climate-smart farming practices. These methods boost productivity and sustainability. They help adapt to changing weather patterns. Farmers can protect their crops and soil. They also reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Simple steps make a big difference.
Planting cover crops, using organic fertilizers, and practicing crop rotation are key. These practices ensure long-term food security. They support the environment too. By embracing these strategies, smallholders can secure their livelihoods. A healthy planet and a stable income are achievable.
Every small change counts. Let’s work together for a sustainable future.



