Nitrogen is one of the most essential elements for life on Earth. It is a major building block of proteins, DNA, and chlorophyll, making it critical for plant growth, animal health, and ecosystem stability. However, despite being abundant in the atmosphere, nitrogen cannot be used directly by most living organisms. This is where the cycling of nitrogen becomes vital.
In this article, we will explore what is the cycle of nitrogen, how it works in nature, the role of bacteria, and why the nitrogen cycle is important for ecosystems, agriculture, and life as a whole.
What Is the Cycling of Nitrogen?
The cycling of nitrogen refers to the continuous movement of nitrogen through the atmosphere, soil, water, plants, animals, and microorganisms. Nitrogen changes its chemical form as it moves through these different components of the Earth system, making it available to living organisms and then returning it back to the environment.
When people ask what is nitrogen cycling, they are essentially asking how nitrogen moves and transforms in nature to support life. This natural recycling process ensures that nitrogen is reused rather than lost, maintaining balance in ecosystems.
What Is the Cycle of Nitrogen?
To clearly answer what is the cycle of nitrogen, it is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms. These transformations allow nitrogen to pass from the atmosphere to living organisms and back again.
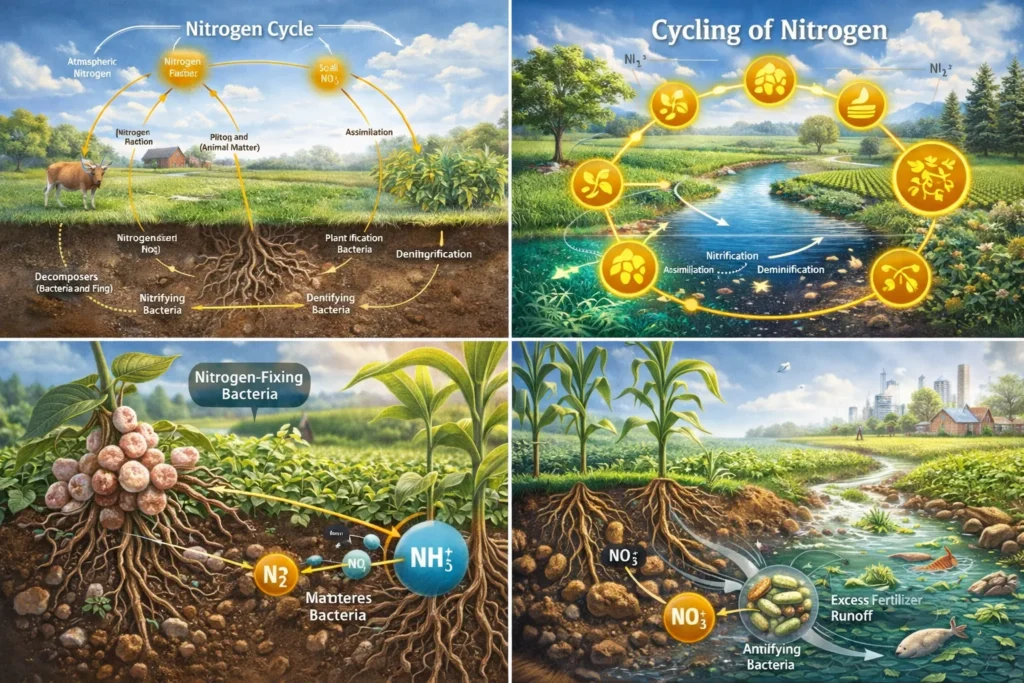
The cycle nitrogen includes several key stages:
- Nitrogen fixation
- Nitrification
- Assimilation
- Ammonification
- Denitrification
Each step plays a crucial role in maintaining nitrogen availability in the environment.
Nitrogen Cycle in Nature
The nitrogen cycle in nature operates continuously, driven by natural forces such as lightning, biological activity, and microbial processes. Even without human involvement, nitrogen would still circulate through air, soil, and water.
In nitrogen cycle nature, microorganisms are the true heroes. Without them, nitrogen would remain locked in the atmosphere and unavailable to plants and animals. Nature has perfected this cycle over millions of years to sustain life.
Major Stages of the Nitrogen Cycle
1. Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the first and most critical step in the nitrogen cycle. Atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is converted into ammonia (NH₃) or ammonium (NH₄⁺), which plants can absorb.
This process occurs through:
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soil and plant roots
- Lightning
- Industrial fertilizers
Here, nitrogen cycle and bacteria work together to initiate life-supporting processes.
2. Nitrification
During nitrification, specialized bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites (NO₂⁻) and then into nitrates (NO₃⁻). These nitrates are the most usable form of nitrogen for plants.
This step highlights how nitrogen cycle ecosystem health depends heavily on microbial activity in the soil.
3. Assimilation
Assimilation occurs when plants absorb nitrates from the soil and use them to create amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll. Animals then obtain nitrogen by eating plants or other animals.
This stage explains what does nitrogen do inside living organisms—it supports growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
4. Ammonification
When plants and animals die or release waste, decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down organic nitrogen compounds into ammonia. This process returns nitrogen to the soil, ensuring continuity of the cycling of nitrogen.
5. Denitrification
Denitrification is the final step where bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas, releasing it into the atmosphere. This completes the nitrogen cycle in nature and prevents excess nitrogen from accumulating in soil and water.
Nitrogen Cycle Ecosystem Connection
The nitrogen cycle ecosystem relationship is deeply interconnected. Every ecosystem—forests, grasslands, wetlands, oceans, and farms—depends on nitrogen cycling for productivity and stability.
When nitrogen cycling is disrupted, ecosystems suffer. Excess nitrogen can cause water pollution, while nitrogen deficiency can limit plant growth and reduce biodiversity.
Importance of Nitrogen Cycle
The importance of nitrogen cycle cannot be overstated. It ensures that nitrogen remains available in usable forms while preventing harmful accumulation.
Some key points highlighting the importance of the nitrogen cycle include:
- Supports plant growth and food production
- Maintains soil fertility
- Regulates ecosystem balance
- Supports microbial life
- Prevents nitrogen loss from ecosystems
In simple terms, without nitrogen cycling, life on Earth would collapse.
Why Nitrogen Cycle Is Important for Plants and Animals
Many people ask why nitrogen cycle is important for living organisms. The answer lies in nitrogen’s biological role.
Nitrogen is essential for:
- Protein synthesis
- DNA and RNA formation
- Enzyme production
- Cell growth and repair
Thus, why is nitrogen cycle important becomes clear—it ensures nitrogen is continuously recycled and made available to sustain life.
Why Is the Nitrogen Cycle Important for Agriculture?
Modern agriculture heavily depends on nitrogen availability. Crops require nitrogen for healthy growth and high yields.
Understanding why is the nitrogen cycle important helps farmers:
- Reduce fertilizer overuse
- Improve soil health
- Minimize environmental pollution
- Promote sustainable farming
Disrupting the nitrogen cycle ecosystem through excessive fertilizer use can lead to soil degradation and water contamination.
Nitrogen Cycle and Bacteria: The Invisible Workforce
The relationship between nitrogen cycle and bacteria is fundamental. Bacteria control nearly every transformation within the cycle.
Types of bacteria involved include:
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
- Nitrifying bacteria
- Denitrifying bacteria
- Decomposers
Without bacteria, nitrogen cycle nature would not function, and nitrogen would remain inaccessible to life.
Human Impact on the Nitrogen Cycle
Human activities such as industrial farming, fossil fuel burning, and deforestation have altered the cycling of nitrogen.
Negative impacts include:
- Water eutrophication
- Soil acidification
- Air pollution
- Climate change contributions
Understanding why is the nitrogen cycle important encourages better environmental management and sustainable practices.
Conclusion
To summarize, the cycling of nitrogen is a life-supporting process that keeps ecosystems functioning and productive. From soil microbes to global ecosystems, every living system depends on nitrogen cycling.
Now that you understand what is the cycle of nitrogen, its stages, and why the nitrogen cycle is important, it becomes clear that protecting this natural process is essential for future food security, environmental health, and sustainability.
Preserving the nitrogen cycle in nature is not just a scientific concern—it is a responsibility shared by all.