Have you ever wondered about the food on your plate and where it comes from? If you’ve browsed the aisles of your grocery store, you’ve likely seen labels like “organic” and “conventional” on produce and other goods.
But what do these terms really mean for you and your family? Understanding the difference between organic and conventional farming can transform how you think about what you eat. This isn’t just about choosing a label; it’s about making informed decisions that impact your health, the environment, and your wallet.
Stay with us as we dive into the world of farming practices, where you’ll uncover the surprising truths and decide what aligns best with your values and lifestyle. Your next trip to the market might just be a game-changer.
Farming Practices
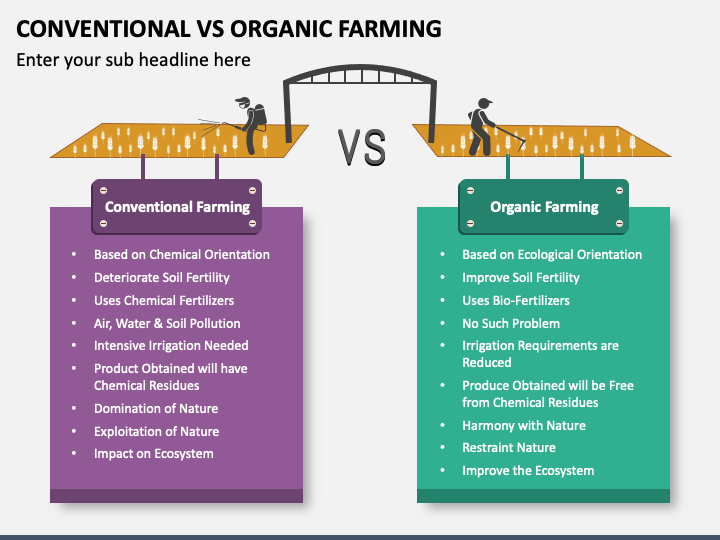
Organic farming uses natural methods to grow crops and raise animals, avoiding synthetic chemicals. Conventional farming relies on chemical fertilizers and pesticides to boost production. Both methods aim to provide food but differ in their environmental impact and resource use.
Understanding the farming practices in organic and conventional farming is crucial for anyone interested in how food production impacts the environment and health. Both methods aim to produce food, but the techniques they employ vary significantly. Let’s dive into these differences and see how they influence the food you eat.
Organic Farming Practices
Organic farming focuses on natural processes and cycles. It uses no synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, relying instead on natural alternatives.
For example, farmers use compost and green manure to enrich soil. This boosts soil fertility without harming the ecosystem.
Crop rotation is a staple in organic farming. It prevents soil depletion and controls pests naturally. This practice ensures crops receive essential nutrients from the soil.
Organic farmers often encourage biodiversity. They plant a variety of crops together to promote a balanced ecosystem. This can help control pests and diseases naturally.
Conventional Farming Practices
Conventional farming relies heavily on technology and chemicals. Synthetic fertilizers and pesticides are common tools to increase yield and manage pests.
These practices can lead to faster crop growth and larger yields. However, they may impact the environment due to chemical runoff into water sources.
Monoculture is typical in conventional farming. Farmers plant large fields with a single crop, maximizing efficiency. But this can lead to soil degradation over time.
Conventional methods often use genetically modified organisms (GMOs). These are engineered for traits like pest resistance or increased yield. While controversial, GMOs can significantly boost productivity.
Comparing Organic And Conventional Practices
Which farming practice resonates more with you? Organic methods emphasize sustainability and environmental health. Conventional methods prioritize efficiency and high yield.
Think about the food choices you make daily. Are they influenced by how these farming practices affect the planet?
The debate between organic and conventional farming practices continues. But understanding their differences helps you make informed choices.
Have you ever considered the journey of your food from farm to table? Next time you shop, ponder the farming practices behind your groceries. Your choices can impact farming trends globally.
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of farming methods is crucial for you as a consumer and for the planet. The debate between organic and conventional farming often revolves around how each affects our environment. As you navigate through your food choices, knowing their implications can guide you toward more sustainable options.
Soil Health
Organic farming enhances soil health by using natural fertilizers and compost. These practices help preserve soil nutrients and prevent erosion. Conventional farming often relies on synthetic fertilizers, which can degrade soil quality over time.
Picture a garden where you nurture plants with compost from your kitchen scraps. Over time, you’ll notice richer soil and healthier plants. This mirrors the benefits organic farms enjoy.
Water Usage
Organic farming typically uses less water due to efficient practices like mulching and drip irrigation. These methods help retain moisture in the soil, reducing the need for constant watering.
Conversely, conventional farming can lead to excessive water use, impacting local water resources. Imagine a farm that relies on heavy irrigation, draining nearby water reserves. Would this be sustainable in the long term?
Pesticide And Chemical Use
Organic farming avoids synthetic pesticides and chemicals, aiming to maintain ecological balance. This means fewer chemicals leaching into water systems, preserving aquatic life.
Conventional farms often use pesticides, which can harm beneficial insects and contaminate water. Think about the times you’ve seen insects buzzing around your garden—each plays a role in the ecosystem.
Biodiversity
Organic farming supports biodiversity by promoting diverse plant and animal life. Crop rotations and intercropping create habitats for various species.
Conventional farming can lead to monocultures, reducing biodiversity. Imagine visiting a farm with just one crop type versus a diverse garden brimming with life. Which scene feels more balanced?
Carbon Footprint
Organic farming may have a lower carbon footprint due to reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Practices such as cover cropping improve carbon sequestration.
Conventional farming often depends on machinery and chemical inputs, which increase carbon emissions. Consider the impact of your choices on climate change.
As you weigh these factors, ask yourself: how do your food choices impact the environment? Making informed decisions can lead to a healthier planet for future generations.
Health Considerations
Organic farming uses natural methods, reducing chemical exposure. Conventional farming often involves synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This difference can impact health, influencing food safety and nutritional value.
When deciding between organic and conventional farming, health considerations often top the list for consumers and farmers alike. Choosing what to put on your plate can have long-term effects on your health. Let’s break down the health aspects of each farming method to help you make more informed choices.
Health Benefits Of Organic Farming
Organic farming methods prioritize natural processes. This often results in crops with fewer pesticide residues. Studies show that organic produce can have higher levels of antioxidants, which are beneficial for your health.
When you buy organic, you’re likely reducing your exposure to harmful chemicals. Ever noticed how organic produce often has a richer taste? That’s due to the nutrient-dense soil practices organic farms use.
Concerns With Conventional Farming
Conventional farming often relies on synthetic chemicals to boost crop yields. This can lead to pesticide residues on the food you eat. Have you ever wondered about the long-term effects of consuming these residues?
Some research suggests potential links between these chemicals and health issues. But, conventional farming can produce more food at a lower cost, making it more accessible to many people.
Impact On Nutritional Value
Organic farming aims to enhance soil health, which can lead to more nutritious produce. Some say organic produce tastes better, but is it just personal preference or a sign of higher nutritional quality?
Conventional farming, on the other hand, focuses on maximizing yield. This can sometimes compromise the nutritional content of the food. Is it worth trading nutrition for quantity?
Personal Experience And Insights
I once switched to a primarily organic diet for a month. I noticed not only did I feel more energetic, but the food seemed more flavorful. Could it be the lack of chemicals or just fresher produce?
Would you consider trying a similar experiment? Sometimes, personal experience is the best way to understand what works for you. It’s not just about what’s on your plate, but how it affects your overall well-being.
Choosing between organic and conventional is personal. What matters most to you when it comes to your health?
Economic Factors
Organic farming often involves higher costs due to natural pest control and labor. Conventional farming typically relies on synthetic chemicals, reducing costs but potentially impacting long-term soil health. Balancing these factors can influence a farmer’s choice between the two methods.
Economic factors play a crucial role in choosing between organic and conventional farming. They impact decisions about production methods, market access, and profitability. Understanding these factors can help you make informed choices about which farming approach is more sustainable and beneficial for your situation.
Cost Of Production
Organic farming often involves higher initial costs. Organic seeds and natural fertilizers can be more expensive than conventional options. However, these costs might be offset by lower long-term expenses due to reduced pesticide and synthetic fertilizer use.
In contrast, conventional farming typically benefits from economies of scale. Large-scale operations can buy inputs in bulk, reducing costs. This often results in lower per-unit costs, making conventional products cheaper in the market.
Market Demand And Pricing
Organic products usually fetch higher prices in the market. Consumers are often willing to pay a premium for food they perceive as healthier or environmentally friendly. This can lead to higher profit margins for organic farmers.
However, the market for conventional products is larger. Conventional products are generally more affordable, appealing to a broader consumer base. This wider market can lead to stable sales and income for conventional farmers.
Subsidies And Government Support
Government policies can significantly influence farming practices. In some regions, subsidies favor conventional farming, providing financial incentives for using chemical fertilizers and pesticides. This can make conventional farming more economically viable.
On the other hand, some governments offer support for organic farming. Grants and subsidies are available to help farmers transition to organic methods. These can help offset the initial higher costs and encourage sustainable practices.
Access To Resources And Technology
Conventional farming often has better access to advanced technology and equipment. This can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, reducing labor costs. Farmers using conventional methods can often produce more with less effort.
Organic farming, however, might require more manual labor. Without synthetic chemicals, organic farmers may need more workers to manage pests and weeds. This can increase labor costs, impacting overall profitability.
Long-term Economic Sustainability
Consider the long-term financial implications of your farming choice. Organic farming can lead to improved soil health and reduced environmental impact. This might enhance land value and ensure long-term sustainability.
Conventional farming, while profitable in the short term, can lead to soil degradation and increased dependency on chemical inputs. This could result in higher costs and lower productivity over time.
Ask yourself, which approach aligns with your long-term goals? Are you willing to invest in sustainable practices that might benefit future generations, or are immediate profits more crucial for you?
Understanding these economic factors can guide you in making a well-informed decision about your farming practices.

Conclusion
Organic and conventional farming differ in many ways. Organic focuses on natural methods. Conventional uses chemicals and machines. Both have benefits and drawbacks. Organic farming supports soil health and biodiversity. Conventional farming often yields more food. Choose based on your values and needs.
Consider health, environment, and cost. Each method plays a role in feeding the world. The choice impacts your health and planet. Understand the differences. Make informed decisions. Your choice matters. Sustainable practices can help future generations. Both farming methods offer solutions.
Balance is key. Choose wisely for yourself and others.



