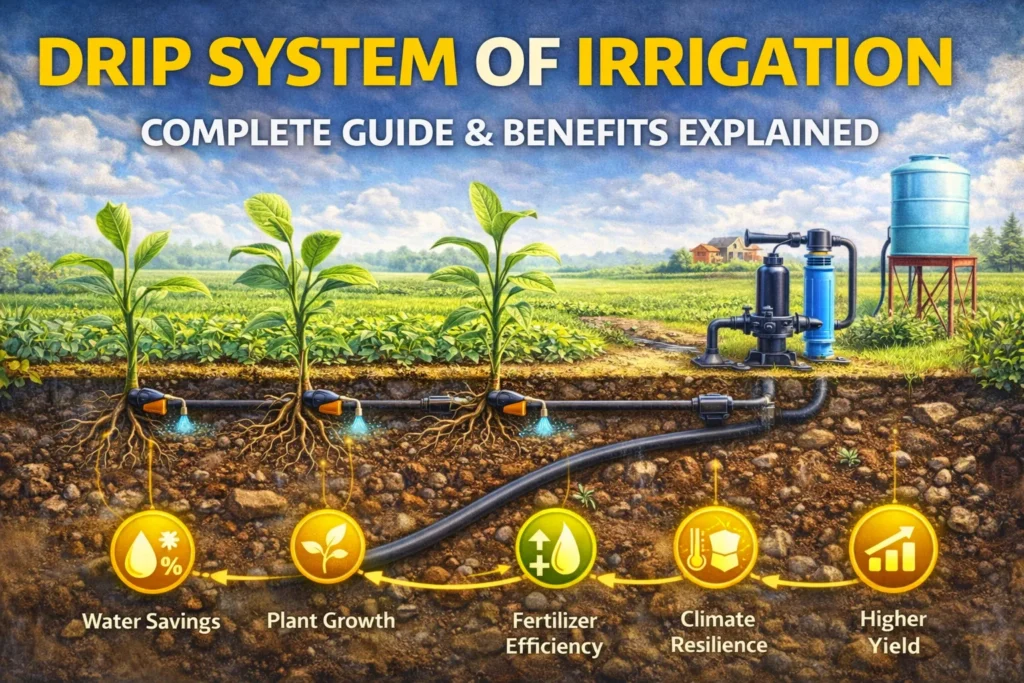
In today’s world of agriculture and gardening, efficient water use is more important than ever. The drip system of irrigation stands out as a game-changer, helping farmers and homeowners save water while boosting plant health. Also known as dripping irrigation or trickle irrigation, this method delivers water directly to the roots, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. Whether you’re curious about what is drip farming or exploring irrigation system types, this article dives deep into everything you need to know. We’ll cover definitions, components, advantages, and more, drawing from reliable sources to give you a full picture.
If you’ve ever wondered what is a drip system or what is drip irrigation, you’re in the right place. This guide aims to explain it all in simple terms, while incorporating practical insights for anyone looking to implement one. By the end, you’ll understand why drip irrigation is revolutionizing farming and landscaping globally.
What is Drip Irrigation?
At its core, what is drip irrigation? It’s a type of micro irrigation systems that allows water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either from above the soil or buried below it. This drip irrigation description highlights its precision: water is delivered through a network of tubes, valves, and emitters, targeting the root zone to reduce evaporation and runoff. Unlike traditional methods that flood fields, the drip system ensures plants get just what they need, when they need it.
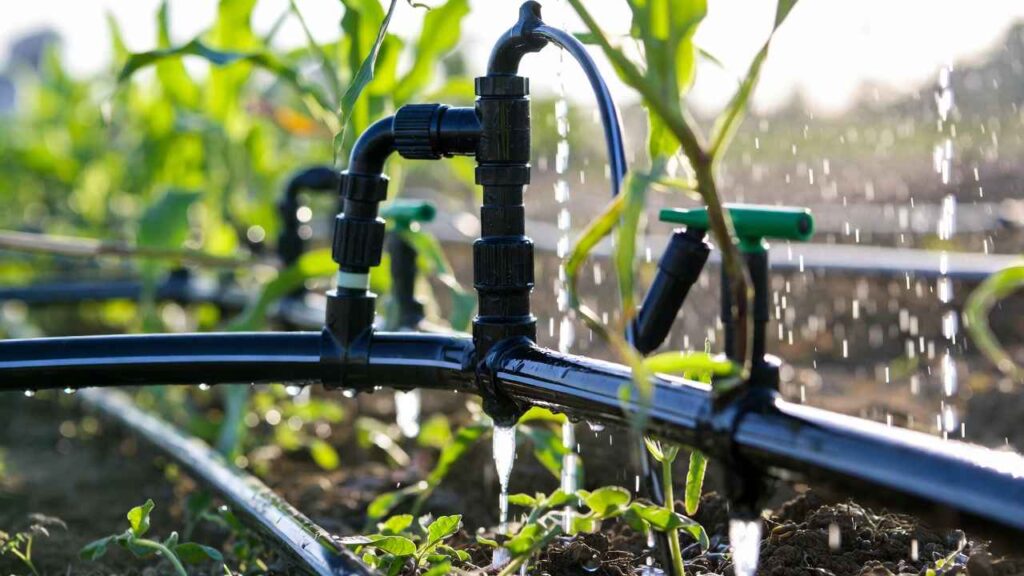

To define drip irrigation, it’s essentially a low-pressure, low-volume watering technique. The drip irrigation meaning revolves around conservation—saving water, nutrients, and energy. If you’re asking what is a drip irrigation or whats drip irrigation, think of it as a dripper system where small emitters release water drop by drop. This drip system definition makes it ideal for arid regions or water-scarce areas.
In simpler terms, define drip system as a targeted approach to hydration. The definition of drip system emphasizes its role in efficient irrigation, where water is applied uniformly and slowly, preventing waste. As per experts, drip irrigation mean the same as trickle irrigation systems, often used interchangeably. For those searching drip irrigation define, it’s a system that can be surface-based or subsurface, adapting to various crops and terrains.
Above is a drip system diagram illustrating flow patterns in a typical setup. This diagram of drip irrigation shows how water moves from the source through pipes to emitters, ensuring even distribution. If you need a visual, such diagram drip irrigation or drip irrigation diagram can help conceptualize the layout.
History and Evolution of Drip Irrigation Systems
The roots of drip irrigation system trace back centuries. Primitive forms appeared in ancient China around the first century BCE, using buried clay pots filled with water to slowly seep into the soil. Modern advancements began in the 19th century in Germany with subsurface clay pipes for irrigation and drainage.
The real breakthrough came in the 1950s in Israel, where Simcha Blass invented the plastic emitter. This led to the formation of Netafim in 1965, pioneering efficient drip irrigation systems. In the US, drip tape was developed in the 1960s, evolving into widespread use by the 1980s. Today, irrigation system drip covers millions of hectares worldwide, with innovations like pulsed systems and smart tech for crops like rice.
For those interested in drip irrigation in hindi or drip system in hindi, it’s commonly called drip sinchai or drip sinchai kya hai, reflecting its global adoption in languages beyond English. This history underscores how trickle irrigation has grown from simple ideas to sophisticated drip irrigation farm solutions.
Types of Drip Irrigation
When considering drip irrigation types or types of drip irrigation, there are several options to suit different needs. The most common is surface drip irrigation type, where emitters are placed on the soil, ideal for row crops.
Subsurface drip system buries the lines below ground, reducing evaporation and weed growth. Drip tape is a popular variant—thin, flexible tubing with built-in emitters, often used in large fields. Then there’s micro-spray or drip sprinkler, which combines dripping with light spraying for wider coverage, like in orchards.
For home use, plant drip irrigation systems might include trickle rings for trees or inline drippers for pots. Understanding these types of drip systems helps in choosing the right one, whether for drip system agriculture or garden beds.
Here’s one of the pictures of drip irrigation system showing it in action on a sugarcane field, demonstrating real-world application. Such drip irrigation system pictures or pictures of types of irrigation can inspire your setup.
Components of a Drip Irrigation System
A well-functioning drip irrigation system relies on key parts of drip irrigation system. Let’s break down the drip irrigation system components or components of a drip irrigation system.
First, the water source connects to a pump or pressurized supply. Filters, like sand separators, prevent clogs. Pressure regulators maintain consistent flow, while valves control distribution. Mainlines carry water to laterals—smaller tubes with emitters.
Emitters, or irrigation drippers, are the heart: they release water at rates like 1-4 liters per hour. Fittings, stakes, and timers automate the process. For fertigation, injectors add nutrients directly.
In a drip irrigation connection, everything links seamlessly. Drip irrigation components also include backflow preventers for safety. If you’re planning a project on drip irrigation, start with a drip irrigation materials list including tubing, emitters, and filters.
For comparison, sprinkler irrigation system components differ, focusing on heads and higher pressure. But for components of drip irrigation, precision is key.
How Does Drip Irrigation Work?
Curious about how does drip irrigation system work or how does drip irrigation work? It’s straightforward yet ingenious.
Water from the source is filtered and pressurized, then flows through mainlines to laterals. Emitters along the lines release droplets slowly, soaking the soil around roots. This explain drip irrigation process minimizes surface wetting, reducing weeds and diseases.
In drip irrigation explained, timing is crucial—timers or sensors activate the system based on soil moisture. For drip irrigation model explanation, imagine a network like veins, delivering “blood” (water) precisely.
A working model of drip irrigation system might use simple hoses for demonstration. Unlike spray irrigation diagram, which shows widespread coverage, drip system of irrigation class 8 lessons often highlight its efficiency for beginners.
This image captures drip irrigation system diagram elements in a field setting, aiding visual understanding.
Advantages of Drip Irrigation
The advantages of drip irrigation are numerous, making it a top choice. First, drip irrigation system advantages include water savings—up to 70% less than traditional methods by reducing evaporation.
Benefits of drip irrigation extend to nutrient efficiency: fertigation delivers fertilizers directly, minimizing loss. Drip irrigation advantages also cover reduced weed growth, as only root zones get wet. Labor costs drop with automation, and it’s adaptable to uneven terrain.
Listing 7 advantages of drip irrigation:
- High water efficiency.
- Lower energy use due to low pressure.
- Reduced soil erosion.
- Fewer diseases from dry foliage.
- Uniform water distribution.
- Safe for recycled water.
- Increased yields.
The drip irrigation advantage in arid areas is profound, as seen in projects like those in Zimbabwe, where drip irrigation kits empower rural communities. Overall, drip irrigation benefits promote sustainability.
Drip Irrigation Advantages and Disadvantages
While benefits shine, consider drip irrigation advantages and disadvantages. Pros include precision and conservation, but advantages and disadvantages of drip irrigation system also note high initial costs and maintenance needs.
Disadvantages: Clogging if not filtered, sun degradation of tubes, and potential salt buildup without leaching. Subsurface systems hide issues, and installation requires expertise.
Yet, for many, pros outweigh cons, especially in drip irrigation importance for water-stressed regions.
Difference Between Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation
What’s the difference between drip and sprinkler irrigation? Drip and sprinkler irrigation vary in delivery: drip targets roots slowly, while sprinkler and drip irrigation sees sprinklers broadcasting water overhead.
In sprinkler and drip irrigation systems, sprinklers cover large areas but lose more to evaporation. Sprinkler drip irrigation hybrids exist, but pure drip irrigation sprinkler system focuses on efficiency.
Table comparing drip system and sprinkler system:
| Aspect | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use | Low, targeted | Higher, broadcast |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% | 70-80% |
| Cost | Higher initial | Lower initial |
| Suitability | Row crops, gardens | Lawns, fields |
| Evaporation | Minimal | Significant |
Drip and sprinkler can complement each other, but for precision, drip wins.
Installation and Layout of Drip Irrigation System
Setting up a drip irrigation system involves planning the layout of drip irrigation system. Start with site assessment: soil, crops, water source.
Install mainlines, then laterals with emitters spaced per plant needs. For drip line irrigation systems, ensure even pressure. Maintenance includes flushing lines and replacing clogged emitters.
In drip irrigation use, automate with timers. Drip irrigation uses span farms to homes, even perennial irrigation system for ongoing crops.
This drip irrigation system pictures example shows installation in a drought-prone area, highlighting practical setup.
Applications and Uses of Drip Irrigation
Uses of drip irrigation are vast: from drip method of irrigation in vineyards to trickle irrigation method for vegetables. In drip water systems, it’s perfect for localized irrigation like greenhouses.
Real-world examples include cabbage under drip irrigation system in Botswana or banana farms in India. Drip full form? It’s not an acronym, but shorthand for drop-by-drop delivery.
For information about drip irrigation or drip irrigation system information, it’s used on over 10 million hectares globally. In drip system information, adaptations for rice reduce emissions.
Challenges and Future of Drip Irrigation Method
Despite benefits, challenges like clogging persist. Future innovations include smart sensors and eco-friendly materials.
In regions like Kyrgyzstan, community projects use drip irrigation for resilience against climate change. As what is the drip irrigation system evolves, it promises even greater sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, the drip system of irrigation offers unparalleled efficiency. From about drip irrigation basics to advanced applications, it’s clear why it’s gaining popularity. Whether for drip and sprinkler irrigation system hybrids or standalone setups, investing in what are drip irrigation systems pays off in yields and conservation.
If you’re planning a project on drip irrigation system, start small and scale up. With proper understanding of water drip meaning—precise, life-giving drops—this method can transform your farming or gardening.