Imagine a world where your farm thrives without depleting natural resources, where every element works in harmony to boost productivity and sustainability. This is not just a dream; it’s the promise of the Integrated Farming System (IFS).
By seamlessly blending different agricultural practices, you can maximize your farm’s potential while nurturing the environment. Curious about how this system can transform your farm into a powerhouse of sustainability? Dive into this article and discover the strategies that can make your farming practices not only more productive but also more eco-friendly.
Stay with us as we explore how IFS can be the key to unlocking a sustainable future for your farm.
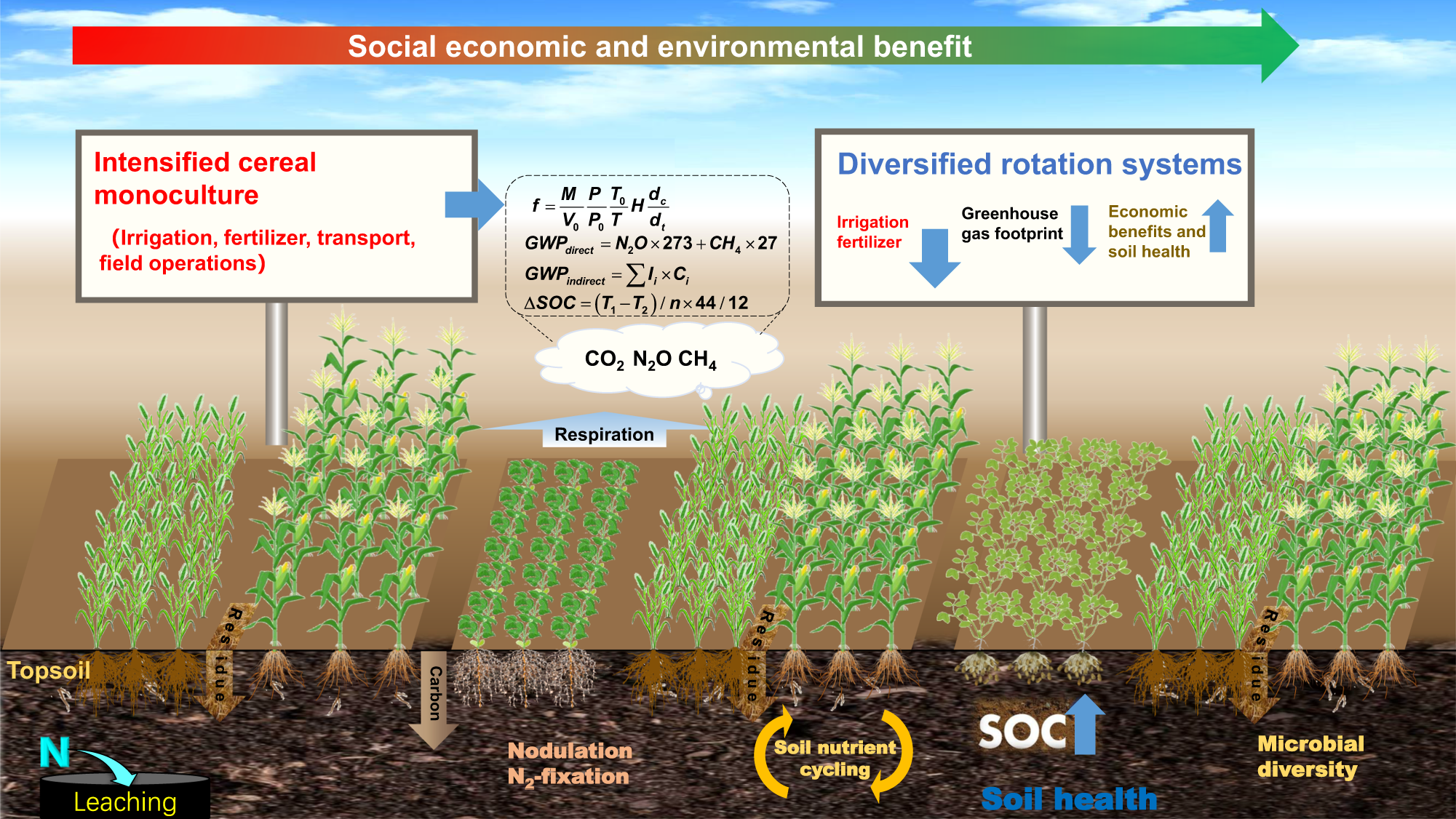
Integrated Farming Basics
Integrated farming combines crops, livestock, and aquaculture for efficient resource use. This system enhances sustainability by recycling nutrients and reducing waste. It supports diverse production while maintaining ecological balance.
Integrated farming is a method that combines different agricultural practices to create a harmonious system, enhancing productivity and sustainability. This approach is more than just growing crops; it’s about creating a balanced ecosystem on your farm. Integrating livestock, crops, and even aquaculture can lead to better resource utilization. It’s a way to make your farming practice more resilient and environmentally friendly.Understanding Integrated Farming
Integrated farming isn’t just a concept; it’s a practical approach. It involves using every part of your farm efficiently. For instance, waste from livestock can be used as fertilizer for crops. This reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can harm the environment. Think about it: your farm can be a self-sustaining ecosystem. By integrating different elements, you reduce waste and increase productivity. It’s about looking at what you already have and finding creative ways to enhance it. Integrated farming can lead to numerous benefits. You might find your soil health improving without synthetic additives. Crop diversity often results in fewer pests. And the best part? Livestock can thrive on crop residues, reducing feed costs. By combining various farming practices, you can create a system that supports itself. This means less reliance on external resources, saving you money and protecting the environment.Practical Steps To Implement Integrated Farming
Start small. You don’t need to overhaul your entire farm overnight. Consider introducing a few chickens or ducks. Their droppings can enrich the soil, and they can help control pests. You could also plant leguminous crops between other plants. These crops fix nitrogen in the soil, enhancing fertility naturally. It’s about making small changes that have a big impact.Challenges You Might Face
Integrated farming isn’t without its challenges. You might struggle with balancing different farm components initially. Managing diverse systems can be tricky, but don’t let that discourage you. Consider attending workshops or connecting with other farmers who have implemented integrated systems. Learning from others’ experiences can be incredibly valuable.Is Integrated Farming Right For You?
Ask yourself: are you ready to embrace a more sustainable farming approach? Integrated farming requires dedication but offers rewarding results. Could this be the change your farm needs? Reflect on your current practices and how they might benefit from integration. The potential for increased productivity and sustainability is immense.
Components Of Integrated Farming
Integrated farming offers a sustainable method to boost agricultural productivity. It combines multiple farming practices into a single system. This approach maximizes resource efficiency and minimizes waste. Understanding the components of integrated farming is key to achieving maximum sustainability.
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry plays a crucial role in integrated farming. Livestock provides manure for crops, enhancing soil fertility. Animals contribute to farm productivity through milk, eggs, and meat. Their waste can be used to produce biogas, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Crop Production
Crop production is the backbone of integrated farming systems. It involves growing diverse crops to improve soil health and reduce pests. Crop rotation is a common practice. It helps in maintaining nutrient balance in the soil. This method increases yield and reduces dependency on chemical fertilizers.
Aquaculture
Aquaculture integrates fish farming with agricultural practices. Fish waste enriches water used for irrigation. This promotes better crop growth. Fish farming also provides an alternative protein source. It contributes to food security and income diversification.
Agroforestry
Agroforestry combines trees and shrubs with crops and livestock. Trees offer shade and protect soil from erosion. They act as windbreaks and improve micro-climate conditions. Agroforestry enhances biodiversity and provides timber and fruit. This diversifies farm products and increases resilience.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is essential in integrated farming systems. Solar panels power irrigation systems and farm machinery. Biogas from animal waste reduces energy costs. These energy sources are sustainable and reduce environmental impact. They ensure energy security for the farm.
Understanding these components can greatly enhance farm sustainability. Each component supports and enriches the other, creating a balanced ecosystem. Integrated farming is a holistic approach to sustainable agriculture.
Benefits Of Integrated Farming
Integrated farming enhances sustainability by combining crops, livestock, and other activities. This approach maximizes resource use and reduces waste. Farmers benefit from diverse income sources and improved soil health.
Integrated farming is a holistic approach that combines various agricultural practices to create a more sustainable and efficient system. By integrating different farming activities, you can maximize resources, reduce waste, and improve the overall productivity of your land. This method is not just about growing crops and raising animals; it’s about creating a balanced ecosystem. What are the tangible benefits that you can reap from this approach? ###Boosted Productivity And Efficiency
Integrated farming allows you to use every inch of your land effectively. By combining livestock with crop production, for example, you can use animal manure as fertilizer, enriching the soil and reducing the need for chemical inputs. This synergy leads to increased yields and healthier produce. Imagine raising chickens alongside your vegetable garden. The chickens feed on pests, reducing the need for pesticides, while their droppings nourish the soil. This cycle leads to healthier crops and a more productive farm. ###Enhanced Biodiversity
Creating a diverse farm environment attracts various species that contribute to a balanced ecosystem. By planting different crops and raising multiple types of animals, you encourage a habitat that supports beneficial insects and natural predators. Think about your farm as a small ecosystem. With varied plant and animal life, you reduce the risk of pest outbreaks and diseases, as they are less likely to spread in a diverse environment. This natural balance saves you time and resources. ###Improved Soil Health
Healthy soil is the foundation of any successful farm. Integrated farming practices, such as crop rotation and cover cropping, help maintain and improve soil structure and fertility. This not only boosts your yields but also reduces erosion and water runoff. Consider alternating between leguminous plants and other crops. Legumes fix nitrogen in the soil, providing essential nutrients for subsequent plantings. This simple practice enhances soil health without the need for synthetic fertilizers. ###Economic Resilience
Diversifying your farming activities can protect you from market fluctuations. If one crop fails or prices drop, other farm products can provide income stability. This diversification makes your farm business more resilient and adaptable. Imagine growing fruit trees alongside your primary crops. Even if your vegetable yields are low one year, the fruit harvest can compensate, ensuring a steady income stream. This strategy offers peace of mind in uncertain times. ###Environmental Benefits
Integrated farming reduces reliance on chemical inputs and encourages natural processes. This leads to cleaner water and air, as well as a reduced carbon footprint. By adopting these practices, you contribute to a healthier planet for future generations. Picture your farm as part of a larger ecosystem. By minimizing chemical use and enhancing natural cycles, you play a crucial role in environmental conservation. How does this align with your personal values and goals? Embracing integrated farming can transform your agricultural practices, making them more sustainable and efficient. What steps will you take today to integrate these benefits into your farming strategy?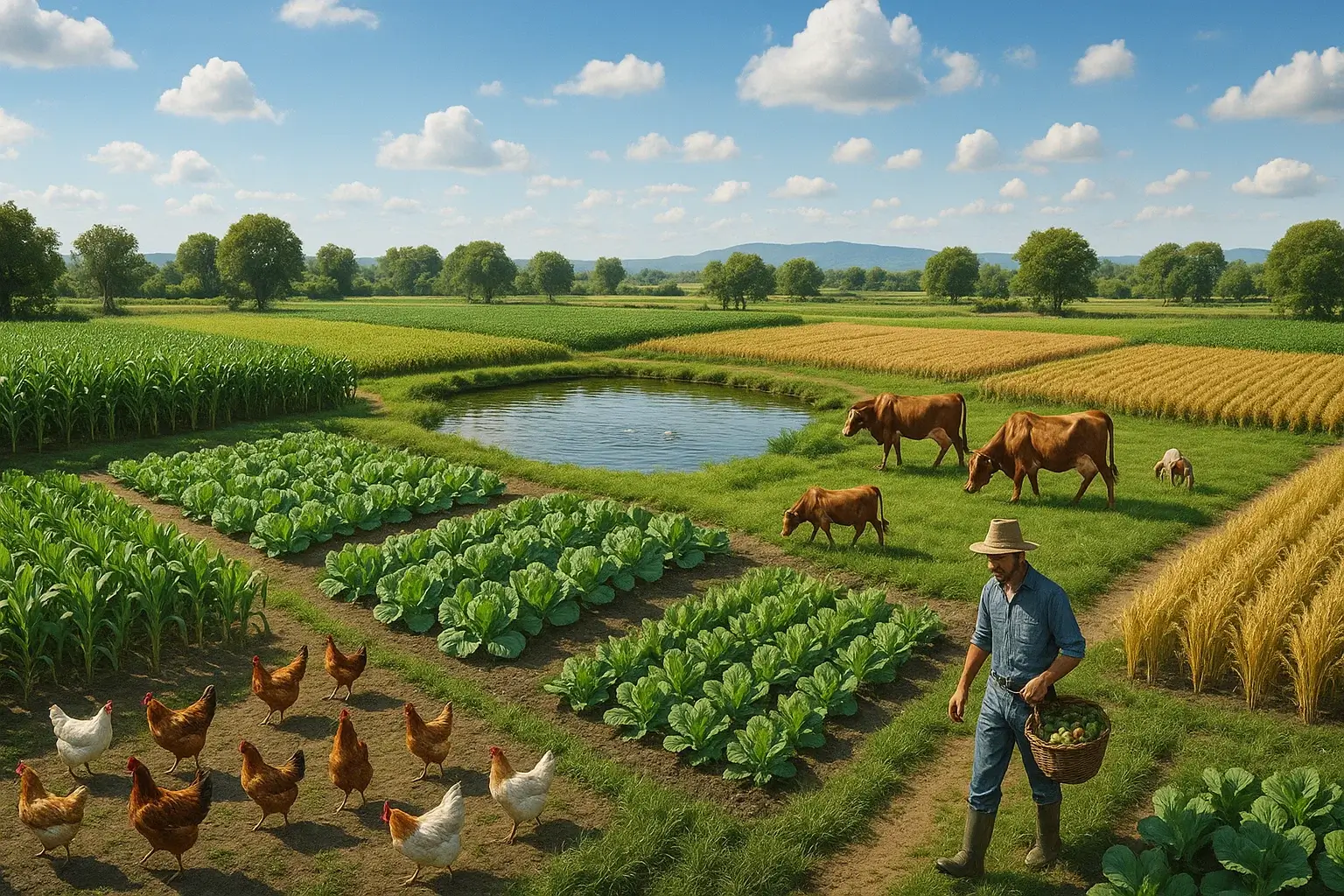
Challenges And Solutions
Integrated farming systems face challenges like resource management and pest control. Solutions include diverse crop rotation and natural pest deterrents. These practices enhance sustainability and boost productivity.
Integrated farming systems aim to achieve maximum sustainability by blending various agricultural practices. However, this approach is not without its challenges. From resource management to technological barriers, farmers often face hurdles that require innovative solutions. Understanding these challenges and how to overcome them is crucial for anyone involved in agriculture.Understanding Resource Limitations
Resource limitations pose a significant challenge in integrated farming systems. Farmers often struggle with limited access to water, land, and capital. These constraints can hinder their ability to implement sustainable practices effectively. One solution is to adopt water-saving technologies like drip irrigation. This technique ensures water reaches directly to the plant roots, reducing wastage. Additionally, practicing crop rotation can help maintain soil fertility, ensuring optimal use of available land.Managing Technological Barriers
Technology plays a vital role in modern agriculture, yet many farmers lack access to necessary tools. The cost of technology and lack of training can impede the adoption of integrated farming methods. Consider investing in affordable technology solutions tailored for small-scale farmers. Mobile apps offering real-time data on weather and crop health can be game-changers. Local workshops can also equip farmers with the knowledge needed to use these technologies effectively.Balancing Biodiversity And Productivity
A common dilemma in integrated farming is maintaining biodiversity while ensuring high productivity. Striking this balance is essential for long-term sustainability. Implementing agroforestry can provide a solution. By planting trees alongside crops, you enhance biodiversity and improve soil health. This method can increase yields while preserving the ecosystem. It’s a win-win for both nature and productivity.Addressing Market Access Issues
Farmers often face difficulties in accessing markets, which can stifle their income potential. Without a stable market, sustainable farming practices may not be economically viable. Creating direct-to-consumer channels such as farmers’ markets can help bridge this gap. Collaborating with local cooperatives can also enhance your market reach. This not only increases income but also fosters community support.Building Resilience To Climate Change
Climate change remains a looming threat to agricultural sustainability. Its unpredictable nature can disrupt farming schedules and reduce yields. Adopting climate-resilient crops can mitigate these effects. Crops that withstand droughts or floods can provide stability in uncertain times. Additionally, implementing weather forecasting tools can help you plan and adapt effectively. Engaging with these challenges requires a proactive mindset. Each problem presents an opportunity to innovate and improve. By tackling these issues head-on, you can pave the way for a more sustainable agricultural future. What steps will you take to overcome these challenges in your farming practice?Conclusion
Integrated farming brings balance to agriculture. It reduces waste and boosts productivity. Farmers benefit from diverse crops and livestock. This system supports long-term soil health. It enhances biodiversity. Communities gain fresh food and job opportunities. Environmental impact lessens significantly. Sustainable practices secure future resources.
Embracing integrated farming is wise. It meets today’s needs and protects tomorrow’s. A harmonious approach to agriculture. This method ensures a healthier planet. It’s a step towards a sustainable future.


