Have you ever wondered how plants drink water? It might seem simple, but there’s fascinating science behind how they do it.
Understanding plant water uptake can transform the way you care for your garden or houseplants. Imagine having the power to optimize their growth just by knowing how they absorb water. This knowledge is not just for botanists or scientists; it’s for anyone who wants lush, healthy plants.
You’ll discover the secrets of how plants manage to transport water from their roots to their leaves. You’ll learn why some plants need more water and others less, and how you can use this information to improve the health of your plants. By the end, you’ll not only be amazed by the incredible process but also equipped with practical tips to nurture your own green oasis. Dive in to unlock the mystery of plant water uptake and make your plants thrive like never before!
Root Structure And Function
Roots are vital for plant survival. They anchor plants and absorb water. Understanding their structure helps us grasp how plants thrive. Roots come in various shapes, each with a unique role.
Root Architecture
The architecture of roots influences water uptake. Roots branch out in soil, increasing surface area. This allows more water absorption. The main root, or taproot, grows deep. It provides stability and reaches water sources below.
Root Hairs
Root hairs are tiny extensions. They grow from root cells. These hairs increase surface area significantly. They penetrate soil particles, accessing more water. Root hairs are vital for efficient water uptake.
Xylem And Phloem
Xylem and phloem are root tissues. They transport water and nutrients. Xylem moves water from roots to leaves. Phloem distributes nutrients throughout the plant. Together, they ensure healthy plant growth.
Role Of Mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae are fungi that associate with roots. They form symbiotic relationships. These fungi extend root surface area. They enhance water and nutrient absorption. Mycorrhizae benefit both roots and plants.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions impact root function. Soil type, moisture, and temperature affect water uptake. Roots adapt to these conditions. They optimize growth and water absorption.

Water Transport Mechanisms
Plants, like silent wonders, efficiently manage their water needs. Their ability to transport water is crucial for survival. This process, known as water uptake, involves intricate mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms reveals the marvel of plant biology.
1. The Role Of Roots
Roots anchor plants and absorb water from the soil. They contain tiny root hairs that increase surface area. This helps in soaking up more water. The absorbed water then moves through the root cells.
2. Capillary Action
Capillary action is a vital water transport method. It occurs when water molecules stick to each other and plant walls. This action allows water to move upwards against gravity. It’s a simple yet effective method.
3. The Xylem Pathway
The xylem is a plant’s water highway. It’s made up of hollow tubes that transport water. Once water reaches the xylem, it travels upwards to the leaves. This journey is essential for plant growth and photosynthesis.
4. Transpiration Pull
Transpiration creates a pull effect. As water evaporates from leaves, it pulls more water upwards. This process is driven by sunlight and wind. It’s a continuous cycle that keeps plants hydrated.
5. Cohesion And Adhesion
Cohesion keeps water molecules together. Adhesion helps them stick to plant walls. Together, they enable smooth water flow within plants. This dual action is crucial for efficient water transport.
Environmental Influences On Water Uptake
When you think about how plants drink water, the environment plays a significant role. Factors like sunlight, temperature, and soil type can affect how efficiently plants take up water. Understanding these factors can help you care for your garden better and ensure your plants thrive.
Light And Water Uptake
Sunlight is a vital component in the water uptake process. More sunlight increases photosynthesis, which in turn boosts a plant’s need for water. If you’ve noticed your plants wilting on a hot, sunny day, it’s because they are working harder and need more water.
On cloudy days, plants require less water. This is because the photosynthesis process slows down. Keep an eye on weather forecasts to adjust your watering schedule accordingly.
Temperature Fluctuations
Temperature changes can also impact water uptake. Warmer temperatures speed up evaporation from the soil and plant leaves. This means your plants might need more frequent watering during hot spells.
In cooler weather, water uptake is slower. Overwatering in such conditions can lead to root rot. Always feel the soil with your fingers to check if it’s dry before adding more water.
Soil Type And Water Retention
The type of soil in your garden can significantly influence water uptake. Sandy soils drain water quickly, meaning plants might need more frequent watering. On the other hand, clay soils retain water longer, reducing the need for frequent watering.
If you’re unsure about your soil type, try a simple test. Squeeze a handful of moist soil; if it crumbles easily, it’s sandy. If it sticks together, it’s clay. Adjust your watering practices based on this observation.
Wind’s Role In Water Loss
Wind can be a sneaky factor in water loss. It increases evaporation from plant surfaces, leading to a higher water requirement. If you live in a windy area, consider creating windbreaks or watering more frequently.
Are your plants in an open, windy spot? If yes, think about relocating them to a sheltered area. This small change can make a big difference in their water needs.
Understanding these environmental influences can transform how you care for your plants. What adjustments will you make in your garden today?

Adaptations In Water-limited Environments
Plants possess unique adaptations for survival in water-limited environments. Their roots efficiently absorb moisture from the soil, using specialized cells. These cells regulate water uptake, ensuring that plants maintain hydration even in dry conditions. This process supports growth and sustains life in challenging climates.
Water scarcity challenges plants in ways that are both fascinating and complex. In water-limited environments, plants have developed unique adaptations to ensure survival. These adaptations allow them to efficiently capture and conserve water, making them remarkable examples of natural ingenuity.Roots: The Silent Water Hunters
Roots are not just anchors; they are sophisticated water hunters. Some plants grow deep taproots that reach underground water sources. Others spread their roots wide and shallow to catch surface moisture from rain or dew. Imagine walking in a desert and stumbling upon a tiny flower. Its roots might be spread out like a network, ensuring it grabs every drop of moisture. Have you ever wondered how your houseplants might mimic these strategies?Leaf Modifications: Conserving Every Drop
Leaves are more than just pretty structures; they are water-saving machines. Many plants have developed thick leaves with waxy surfaces to minimize water loss. Others, like succulents, store water within their leaves. Think about a cactus. Its leaves have transformed into spines, reducing surface area to prevent evaporation. What changes could you make in your home to conserve water as effectively as these plants do?Stomatal Adjustments: Breathing Wisely
Stomata are tiny openings on leaves for gas exchange, and their function is crucial. In water-limited environments, plants control these openings to reduce water loss. They might close during the day to preserve moisture and open at night when temperatures drop. Consider this: adjusting your breathing during exercise saves energy. Similarly, plants adjust their stomatal activity to save water. Could you apply such strategic thinking to your daily routines?Water Storage Techniques: Preparing For Drought
Some plants store water in their stems or roots, preparing for dry spells. These reservoirs act like natural water bottles, ensuring survival during prolonged droughts. Imagine living in a place with unpredictable rainfall. Having a reserve of water, just like these plants, could be a lifesaver. How can you create a buffer for your own needs?Plants in water-limited environments inspire us with their resilience and adaptability. By understanding their strategies, you can learn to be resourceful in conserving water. What plant adaptation will you try to incorporate into your life?
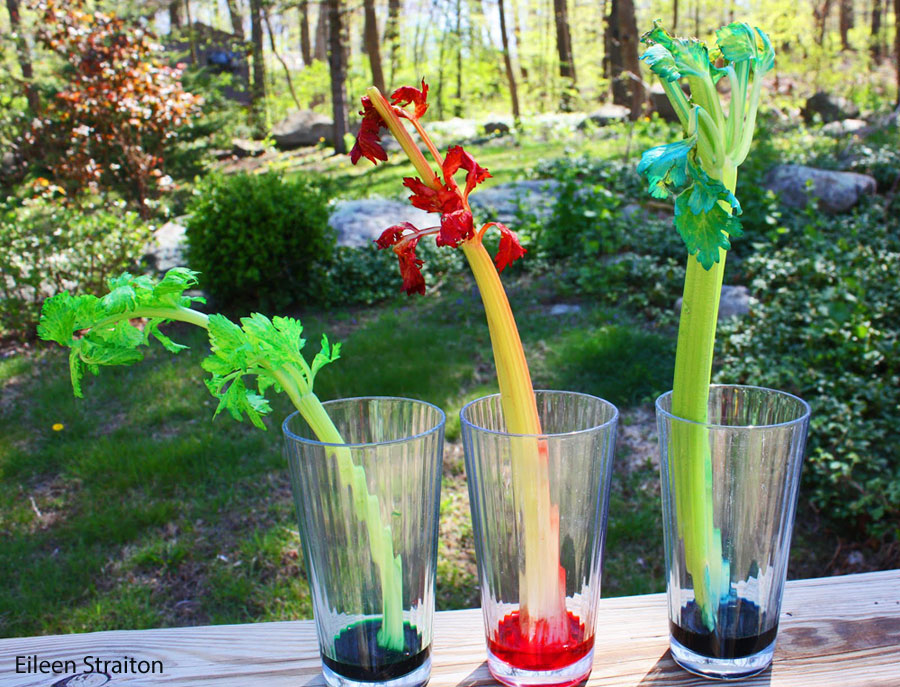

Conclusion
Plants drink water in amazing ways. Roots are the key players. They soak up water from the soil. This water travels up through the plant. Cells and tissues help in this journey. Each part plays its role. Leaves release some water back into the air.
This cycle keeps plants alive and thriving. Understanding this process helps us care for plants better. Whether in gardens or farms, water is crucial. So next time you water plants, think of their incredible system. Appreciate nature’s design in every leaf and root.